What is Biomass Fuel and How Does It Work?
🌱 Biomass Fuel: The Future of Sustainable Industrial Energy
What is Biomass Fuel and How Does It Work?
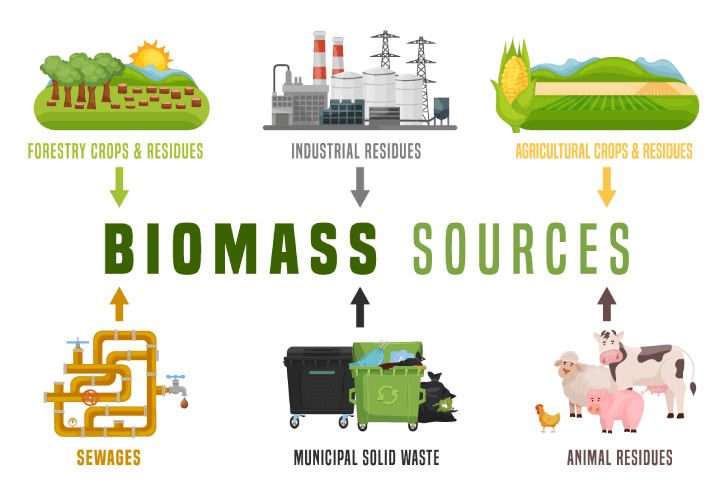
Biomass fuel is a renewable, organic material derived from plants and animal waste that can be used as a sustainable energy source. Common forms include biomass pellets, biomass briquettes, and agricultural residues. These fuels are burned in biomass boilers, biomass burners, or biomass stoves to generate heat or power, making them an excellent alternative to fossil fuels.
🌾 What is Biomass Fuel?
Biomass fuel is any type of energy source derived from organic material, such as:
- Agricultural residues (rice husk, straw, sugarcane bagasse)
- Wood and sawdust
- Animal waste (cow dung, poultry litter)
- Industrial and municipal organic waste
- Energy crops (like miscanthus, switchgrass)
These materials are renewable, and when processed into fuels like pellets, briquettes, biogas, bioethanol, or biodiesel, they become powerful sources of heat, electricity, or transport fuel.
⚙️ How Does Biomass Fuel Work?
Biomass fuels release energy through different conversion processes, depending on the fuel type and application:
🔥 1. Combustion (Burning for Heat or Power)
- Biomass (like wood pellets or briquettes) is burned in a boiler or furnace.
- The heat produced:
- Can be used directly for industrial processes.
- Or to generate steam for turning turbines → electricity generation.
🔧 Used in: Industrial boilers, power plants, home heating
🔁 2. Gasification
- Biomass is heated in low-oxygen conditions.
- Produces syngas (a mix of CO, H₂, CH₄), which can be burned like natural gas for power.
🔧 Used in: Biomass gasifiers, gas engine generators
💨 3. Anaerobic Digestion (Biogas Production)
- Organic waste is broken down by bacteria in oxygen-free digesters.
- Produces biogas (mainly methane) used for cooking, heating, or power.
- Byproduct: Organic slurry used as fertilizer.
🔧 Used in: Rural biogas plants, urban food waste digesters
🛢️ 4. Liquid Biofuel Conversion
- Biodiesel: Made from vegetable oils, animal fats, or used cooking oil.
- Bioethanol: Made from sugarcane, corn, or cellulosic biomass.
- These fuels are used in vehicles or generators.
🔧 Used in: Blended transport fuels (like E20), diesel gensets
✅ Benefits of Biomass Fuel
- Renewable & locally sourced
- Carbon-neutral when sustainably managed
- Converts waste into energy
- Supports rural economies
- Reduces dependence on coal, LPG, or diesel
What Types of Biomass Energy Solutions Biomass Offer?
🔥 1. Biomass for Thermal Energy (Heat Production)
- Application: Boilers, kilns, heating systems, industrial furnaces
- Fuel Types: Wood chips, pellets, briquettes, agro-waste (like rice husk, sawdust)
- Benefits: Reduces dependence on coal or fossil fuels in process heating
⚡ 2. Biomass for Electricity Generation
- Application: Biomass power plants, cogeneration (CHP), gasifiers with engines/turbines
- Technologies:
- Direct combustion (in boilers with steam turbines)
- Gasification (produces syngas to run generators)
- Anaerobic digestion (biogas for gensets)
- Fuel Types: Agro-waste, wood waste, poultry litter, municipal organic waste
💨 3. Biogas Production (from Anaerobic Digestion)
- Application: Cooking, electricity generation, vehicle fuel (after purification)
- Feedstock: Cow dung, food waste, agricultural waste, municipal sludge
- Byproducts: Biogas (CH₄ + CO₂) and organic fertilizer (digestate)
🟤 4. Biomass Pellets and Briquettes
- Use: Fuel for domestic, industrial boilers, and small-scale power plants
- Raw Materials: Sawdust, rice husk, straw, peanut shells, sugarcane bagasse
- Advantages: High density, easy to store/transport, cleaner combustion
⛽ 5. Biofuels (Liquid Biomass Fuels)
- Types:
- Biodiesel (from used cooking oil, non-edible oilseeds like Jatropha)
- Bioethanol (from sugarcane, molasses, corn, cellulosic waste)
- Bio-CNG (purified biogas used for vehicles)
- Applications: Transport, generators, industrial heating
🔄 6. Combined Heat and Power (CHP) from Biomass
- Technology: Uses one process (like combustion or gasification) to simultaneously produce electricity and useful heat
- Ideal for: Agro-industries, dairies, food processing units, eco-industrial parks
🌱 7. Waste-to-Energy Solutions (Bioenergy from Waste)
- Sources: Municipal solid waste, industrial organic waste, food/agri waste
- Output: Biogas, syngas, RDF (Refuse Derived Fuel), or compost
- Goal: Sustainable waste management + energy recovery
- Biomass Fuel: Clean and renewable, suitable for industrial and domestic heating.
- Biomass Pellets: Densified, high-efficiency fuel perfect for boilers and heating systems.
- Biomass Briquettes: Eco-friendly, compact fuel with high calorific value.
- Biomass Burner: Advanced combustion technology designed for optimal efficiency.
- Biomass Boiler: Custom-designed systems for steam and hot water applications.
- Biomass Stove: Ideal for small-scale heating with clean emissions.
- Biomass Heating System: Complete heating solutions tailored for homes, factories, and institutions.
- Industrial Biomass Fuel: Specially processed fuel for large-scale operations.
Why Choose Biomass Energy?
✅ 1. Renewable & Sustainable
- Biomass comes from organic sources like crop waste, wood, and animal manure.
- Unlike fossil fuels, it regrows or regenerates, making it sustainable over time.
✅ 2. Reduces Waste
- Converts agricultural, forestry, and municipal waste into useful energy.
- Helps manage residue like rice husk, sawdust, bagasse, cow dung, and food waste.
✅ 3. Carbon-Neutral (Low Emissions)
- Biomass releases only the CO₂ absorbed during the plant’s lifecycle—no net increase in atmospheric carbon (if sourced sustainably).
- Replaces fossil fuels and cuts greenhouse gas emissions.
✅ 4. Energy Independence & Rural Empowerment
- Locally available feedstock reduces reliance on imported fuels.
- Creates jobs in rural areas—in collection, processing, and operation.
- Supports energy access in off-grid or underserved regions.
✅ 5. Versatile Applications
- Used for electricity generation, industrial heat, cooking fuel, and even as transport fuel (bioethanol, biodiesel, bio-CNG).
- Powers everything from a rural stove to a large factory boiler.
✅ 6. Economical & Scalable
- Low-cost raw materials (agri-waste, wood chips, dung, etc.)
- Flexible systems for small-scale homes to industrial-scale power plants
- Can replace costly LPG, diesel, and coal in industries.
✅ 7. Government Incentives & Policies
- Supported under India’s National Bioenergy Programme, with capital subsidies, tax benefits, and carbon credits.
- Aligned with India’s net-zero and clean energy goals.
✅ 8. Circular Economy Impact
- Biomass promotes a zero-waste system by reusing residues.
- Byproducts like biochar, ash, or digestate can be used as fertilizer.
- Sustainable Alternative to Fossil Fuels: Biomass is carbon-neutral and helps reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
- Eco-Friendly Fuel Options for Industries: Switch to cleaner combustion without sacrificing performance.
- Cost-Effective Heating: The cost of biomass fuel per ton is significantly lower than coal or oil in the long run.
- Reliable Biomass Fuel Suppliers Near You: Biomass supply to various regions, ensuring timely and bulk delivery.
- Energy Independence: Reduces dependency on imported fossil fuels.
🔥 How Biomass Pellets Provide solutions for Industrial Heating?
🔹 1. Combustion in Biomass-Fired Boilers
- Biomass pellets (made from sawdust, agri-waste, etc.) are burned in specially designed biomass boilers or thermic fluid heaters.
- The combustion generates hot water, steam, or hot air for industrial use.
✅ Suitable for:
- Food & beverage industry
- Dairy and milk processing
- Pulp & paper mills
- Pharmaceuticals
- Textile dyeing
- Chemical manufacturing
- Brick & ceramic kilns
⚙️ Heating System Configuration
Input: Biomass Pellets (or briquettes)
Equipment:
- Biomass Boiler / Thermopack / Furnace
- Pellet/Briquette Feeder System
- Air Preheaters, Cyclones, or ESP for emissions
Output: - Hot Water / Steam / Hot Air
♻️ Alternate Biofuels for Industrial Heating
🔹 Bio-CNG:
- Purified biogas used in industrial burners for high-temp heating.
🔹 Biodiesel:
- Used in diesel burners or gensets, often blended with regular diesel.
🔍 Why Industries Choose Biomass for Heating
| Feature | Advantage |
| 🌱 Eco-Friendly | Lower CO₂ emissions; qualifies for carbon credits |
| 💸 Cost-Effective | 20–50% cheaper than diesel or furnace oil |
| 🇮🇳 Made in India | Uses local agri-residues—supports rural economy |
| 🔧 Customizable Systems | Can retrofit existing boilers with biomass burners |
| 🏭 24/7 Heating | Suitable for continuous operations |
📈 Example:
A textile unit using 500 kg/hour of steam replaced its diesel-fired boiler with a biomass pellet-fired unit, cutting fuel costs by ~40% and reducing CO₂ emissions by over 1,000 tons/year.
Industries across India are switching to biomass energy for industrial heating due to rising fossil fuel costs and environmental regulations. Our biomass heating systems for factories are designed to deliver consistent heat for processes like drying, curing, and steam generation.
✅ How Biomass Pellets Superior vs. Coal & Firewood?
| Feature | Biomass Pellets | Coal | Firewood |
| 🌍 Eco-Friendliness | Carbon-neutral, low emissions | High CO₂, SOx, NOx emissions | Emits smoke, incomplete combustion |
| 🔥 Calorific Value | 3800–4500 kcal/kg (consistent) | 5000–6500 kcal/kg (high but dirty) | 2500–3500 kcal/kg (variable) |
| 💨 Ash Content | Low (≤5%) | High (10–25%) | High (5–15%) |
| 📦 Moisture Content | Low (≤10%) – dried during production | Variable (5–12%) | High (20–60%) – needs drying |
| 🏭 Combustion Efficiency | High – uniform burn | Moderate – clinkers & slag | Low – smoky, inefficient burn |
| 🧼 Storage & Handling | Clean, compact, easy to transport | Dirty, polluting, hard to handle | Bulky, prone to moisture & pests |
| 🔁 Renewable | Yes – from agri/wood waste | No – finite fossil resource | Yes – but not always sustainably sourced |
| 🔧 Boiler Compatibility | Works in automated feed systems | Requires heavy-duty boiler | Only in basic furnaces or stoves |
| 📉 Emission Compliance | Easily meets pollution control norms | Violates many air quality limits | Creates visible smoke & particulates |
🌿 Why Biomass Pellets Are Superior
🔹 1. Cleaner Combustion
- Very low sulfur, nitrogen, and heavy metal content
- Complies with pollution control board (PCB) standards
🔹 2. Higher Efficiency
- Pellets are densified, dry, and uniform, ensuring complete combustion
- No clinkers or ash buildup like coal
🔹 3. Environmentally Responsible
- Made from renewable agricultural and forestry waste
- Supports carbon neutrality (plants reabsorb emitted CO₂)
🔹 4. Operational Convenience
- Automatic feeding possible (unlike firewood)
- Minimal storage space; easier logistics
🔹 5. Supports Green Certifications
- Helps industries achieve ISO 14001, Green Building, and carbon credit eligibility
📌 Summary
🔥 Biomass Pellets = Clean, Efficient, and Renewable
🪨 Coal = Dirty, Declining, and Polluting
🌲 Firewood = Traditional but Inefficient
✅ Benefits of Biomass Pellet Use in Industrial Boilers?
🔥 1. Clean & Efficient Combustion
- Biomass pellets have low moisture (<10%) and uniform size, ensuring complete and efficient burning.
- High calorific value (~4000 kcal/kg) comparable to mid-grade coal.
🌍 2. Environmentally Friendly
- Carbon-neutral fuel: emits only the CO₂ absorbed during plant growth.
- Lower SOx, NOx, and PM emissions compared to coal or firewood.
- Helps industries meet Pollution Control Board norms and reduce carbon footprint.
💸 3. Significant Cost Savings
- Biomass pellets are typically 20–50% cheaper than diesel, LPG, or furnace oil.
- Lower operational costs due to reduced slagging and ash disposal needs.
🏭 4. Fuel Handling and Storage Advantages
- Compact, dense pellets are easy to store, handle, and transport.
- Clean and dust-free – unlike coal or firewood.
⚙️ 5. Compatible with Existing Boilers
- Can be used in:
- Retrofitted coal or oil boilers and Dedicated biomass boilers
- Suitable for steam generation, process heating, or thermic fluid systems.
♻️ 6. Supports Waste-to-Energy and Circular Economy
- Made from agri-residues, sawdust, or organic waste, diverting waste from landfills.
- Encourages sustainable energy use in rural and urban supply chains.
🌱 7. Eligible for Green Certifications & Subsidies
- Helps achieve ISO 14001, green building ratings, and ESG goals.
- Can qualify for carbon credits, government bioenergy subsidies, and renewable energy certificates (RECs).
👨🔧 8. Low Maintenance and Cleaner Operation
- Less ash and slag means longer boiler life and reduced downtime.
- Automatable feeding and combustion systems for consistent performance.
📈 9. Improves Corporate Sustainability Profile
- Enhances your brand’s eco-conscious image.
- Meets rising demand for low-emission supply chains from global clients.
🔋 10. Energy Security & Price Stability
- Locally available feedstock protects against fossil fuel price shocks.
- Reduces dependency on coal imports or volatile oil markets.
🧾 Example:
A textile mill using 1,000 kg/h steam saved ₹35–40 lakh/year after switching from diesel to biomass pellets, while reducing emissions by over 70%.
✅ How Biomass Fuel: Reliable Supply Across India?
🚛 1. Widespread Raw Material Availability
India generates 600+ million tons/year of biomass waste:
- Rice husk, straw, bagasse (Uttar Pradesh, Punjab, Haryana, Maharashtra)
- Sawdust, wood chips (Gujarat, MP, Karnataka)
- Coconut shell, groundnut shells (Tamil Nadu, Andhra, Kerala)
- Cow dung, poultry litter (Pan-India)
This ensures year-round raw material access across regions.
🏭 2. Large Network of Pellet & Briquette Manufacturers
Over 1,000+ biomass pellet & briquette producers are active in India, especially in:
- Punjab, Haryana, UP, MP (Agro-pellets, rice husk, straw)
- Gujarat, Maharashtra, Karnataka (Wood pellets, sawdust)
- Tamil Nadu, Andhra, Telangana (Coconut shell, sugarcane waste)
They offer bulk contracts, custom pellet sizes, and on-time deliveries.
📦 3. Logistics & Pan-India Distribution
- Dedicated biomass logistics companies and aggregators now offer pan-India delivery by road and rail.
- Storage silos, bulk bags, and auto-feeding systems ensure smooth plant operations.
- Inventory management systems now help ensure zero downtime.
🧪 4. Quality Standards & Certifications
Top biomass fuel producers follow:
- IS/ISO standards for pellet density, moisture (<10%), ash (<5%)
- Regular testing for calorific value, ash content, and moisture
- Long-term contracts ensure price and quality stability
📉 5. Stable Pricing Compared to Fossil Fuels
- Biomass pellets are not subject to international crude price volatility
- Fuel prices remain relatively stable year-round
- You can lock-in long-term rates with major suppliers
📌 Summary:
✅ Consistent Supply
✅ Pan-India Logistics
✅ Standardized Quality
✅ Stable Pricing
✅ Reliable Industrial Fuel Source
🌾 How Biomass industry Creating Employment Opportunities in India?
- Biomass Fuel Production
- Pellet and briquette manufacturing units:
These factories require a skilled workforce to manage production lines, packaging, and logistics. Jobs are created in urban and rural areas, where agricultural residues (like rice husk, straw, and bagasse) are collected, processed into pellets/briquettes, and distributed. - Factory roles: Production managers, machine operators, quality control personnel, and logistics staff are employed in biomass pellet and briquette plants.
- Pellet and briquette manufacturing units:
- Collection & Supply Chain
- Waste collection: Many rural farmers and laborers are employed in collecting crop residues, forestry waste, and other organic materials. These materials are then transported to biomass processing plants or sold to fuel manufacturers.
- Transportation and logistics: Drivers, warehouse managers, and logistics coordinators play a key role in moving biomass from farms to processing units and delivery points, creating an organized supply chain network.
- Operation & Maintenance
- As industries and power plants adopt biomass-based boilers, gasifiers, and cogeneration units, there’s a growing need for trained workers to operate and maintain these systems. This includes jobs for technicians, engineers, and plant operators.
- Research and Development (R&D)
- The biomass industry is seeing an uptick in R&D jobs related to improving fuel efficiency, developing new biomass energy solutions, and enhancing processing technologies. Universities and energy organizations employ researchers, engineers, and innovators.
🌱 How Biomass industry Generating Additional Revenue for Farmers?
- Sale of Agricultural Residues
- Farmers can earn additional income by selling agricultural residues (like rice husk, wheat straw, sugarcane bagasse, etc.) to biomass fuel manufacturers or bioenergy companies.
- Contract farming or outreach programs can encourage farmers to grow energy crops (like Jatropha or Castor) for biofuel production, providing a direct income stream.
- Agri-Waste Utilization
- Instead of burning leftover crop residues (which is harmful to the environment), farmers can sell the biomass to pellet manufacturers, turning waste into revenue while avoiding penalties related to air pollution.
- Co-Generation and Biomass Power Plants
- Farmers near biomass power plants or co-generation units can provide raw materials (like animal waste, crop residues) for energy production. Some farmers also establish partnerships with biomass power producers, which pay for the biomass on a regular basis, creating a stable income for farmers.
- Biochar and Fertilizer Sales
- By-products from biomass energy production, like biochar, can be used as fertilizer or sold to farmers, creating an additional source of revenue. The nutrient-rich ash produced from burning biomass can also be used for soil health improvement, allowing farmers to benefit from improved crop yield and quality.
- Carbon Credit Programs
- Biomass-based energy systems can qualify for carbon credits. These programs allow farmers or energy producers to earn revenue by reducing greenhouse gas emissions through the use of biomass energy, improving both environmental and financial returns.
📊 How Biomass industry supports Economic and Social Impact?
- Farmers’ Income Boost: By participating in the biomass economy, farmers can diversify their income streams beyond traditional crop farming, reducing seasonal income fluctuations.
- Job Creation in Rural Areas: Biomass businesses create rural jobs, leading to improved standards of living and reducing migration to cities.
- Sustainable Farming Practices: Farmers are encouraged to adopt sustainable agricultural practices like crop rotation and growing bioenergy crops, benefiting both the environment and their profits.
✅ Benefits of Biomass Fuel?
🔁 1. Renewable & Sustainable
- Derived from agricultural waste, forestry residues, and organic matter
- Constantly replenishable—not a fossil resource
🌍 2. Environmentally Friendly
- Carbon-neutral: Biomass absorbs CO₂ during growth and releases it during combustion, maintaining balance
- Lower emissions of sulfur dioxide (SO₂), nitrogen oxides (NOx), and particulate matter than coal or diesel
💸 3. Cost-Effective
- Generally 20–50% cheaper than fossil fuels like LPG, diesel, or coal
- Lower operational and maintenance costs for compatible equipment
🚛 4. Readily Available in India
- India produces hundreds of millions of tons of biomass waste annually
- Reliable supply chain of pellets, briquettes, and biofuels across all regions
🏭 5. Industrial Versatility
- Used in boilers, kilns, thermic fluid heaters, gasifiers, and even electricity generation
- Suitable for textile, food processing, pharma, packaging, cement, brick kilns, and more
🧪 6. Standardized & Efficient
- Biomass pellets and briquettes are uniform in size, moisture, and calorific value
- Ensure clean, high-efficiency combustion in modern industrial systems
🧼 7. Reduces Waste
- Converts agricultural and industrial waste into energy
- Reduces open burning, landfill use, and methane emissions
📉 8. Lower Ash & Cleaner Operation
- Less ash generation than coal or wood
- Easier ash handling and disposal; some byproducts (e.g., biochar) are reusable as fertilizer
🏆 9. Supports Green Certifications & ESG Goals
- Helps meet ISO 14001, LEED, RE100, or carbon credit programs
- Boosts a company’s sustainability profile and market reputation
🌱 10. Empowers Rural Economy
- Encourages rural entrepreneurship in biomass collection and fuel production
- Generates local jobs and supports farmer income from crop residue sales
📉 11. Stable Pricing
- Biomass prices are more stable than international fossil fuel prices
- Long-term contracts help control energy cost volatility
🧭 12. Energy Security
- Reduces dependency on coal, oil, and gas imports
- Improves national and local energy independence
📌 Summary:
Biomass fuel is clean, renewable, affordable, and abundant—making it a practical energy solution for sustainable industrial growth and rural empowerment.
🚀 Supporting Startups in the Biomass Sector
1. Business Opportunities in Biomass Fuel Production
- Biomass Pellet & Briquette Production: Startups can enter the biomass industry by establishing small to medium-scale pellet production units using agriculture waste (like rice husk, sugarcane bagasse, and sawdust). With rising demand for clean energy, the market potential for pellets is huge.
- Biogas Plants: Startups can set up biogas production plants to convert organic waste (from farms, food processing units, or municipal waste) into biogas for cooking or power generation. This offers a circular economy model for energy.
- Bioenergy Systems: Startups can create businesses that provide biomass-powered generators, boilers, and heating systems to industries in rural areas.
2. Technology Solutions for Biomass Utilization
- Tech-driven biomass solutions: Startups can develop platforms or apps that connect farmers with biomass fuel manufacturers, offer data analytics on energy consumption, or provide IoT-based monitoring systems for efficient biomass management.
- Efficient Processing Technologies: Innovations in drying, densification, and gasification processes are driving more efficient biomass fuel production. Startups can focus on improving these technologies to enhance energy output or reduce costs for farmers and manufacturers.
3. Access to Government Schemes and Grants
- The Indian government provides support to biomass startups through various schemes like MNRE (Ministry of New and Renewable Energy), NABARD, and Startup India. These schemes offer:
- Subsidies on machinery for biomass processing
- Financial support for setting up biomass-based power plants or pellet plants
- Tax incentives for clean energy businesses
4. Sustainability-Focused Investment
- Biomass-based startups are attracting impact investors and venture capitalists focusing on clean energy and sustainability. Biomass offers startups an opportunity to access green funding through crowdfunding platforms, social impact funds, and private equity investors.
🌾 Supporting Farmer Producer Organizations (FPOs)
1. Biomass Residue Collection and Supply Chain
- FPOs can play a central role in aggregating agricultural waste (e.g., straw, husks, and stubble) from small farmers and selling it to biomass fuel producers. This creates a supply chain model that gives farmers direct market access, bypassing middlemen and ensuring better prices for their residues.
- FPOs can also manage biomass storage and distribution of fuel, which helps ensure consistency in supply and quality of the biomass.
2. Setting up Biomass-Based Power Plants
- FPOs can collaborate to build small biomass-based power generation units or community bioenergy projects. These plants can convert agricultural residues into electricity or heat, which can then be used to power local businesses or sold to the grid.
- These projects can be scaled up to include biogas plants for clean cooking solutions, where FPOs handle the collection of organic waste and operate the plants, creating an additional source of income for members.
3. Creating Jobs and Employment in Rural Areas
- Biomass-based businesses provide new job opportunities in rural areas. FPOs can establish biomass pellet production units, waste collection systems, and biogas plants, offering employment to locals in operations, logistics, maintenance, and sales.
- These ventures also reduce migration to cities, as local communities benefit from stable incomes linked to biomass enterprises.
4. Cooperative Biomass Projects
- FPOs can join forces to establish cooperative biomass initiatives where the profits from biomass fuel production are shared among members. This model supports shared infrastructure and joint marketing, providing a sustainable business model for small-scale farmers.
- Revenue from biomass energy and byproducts (like biochar or organic fertilizers) can be reinvested in community development and capacity building.
💡 Key Areas Where Biomass Helps FPOs and Startups:
- Revenue Generation from Waste: Biomass transforms agricultural waste (previously burnt or discarded) into a lucrative business opportunity, adding value to byproducts.
- Sustainability and Environmental Impact: Biomass-based businesses provide clean energy solutions, reduce air pollution, and support carbon footprint reduction.
- Access to Technology & Finance: Government schemes, private investors, and new technologies are enabling FPOs and startups to scale and innovate.
- Employment Generation: Creating jobs in rural areas by setting up biomass collection, processing, and power generation systems.
- Market Linkages: Startups and FPOs benefit from direct access to markets for biomass fuels and energy products, ensuring consistent demand.
🌱 Example:
In Maharashtra, a group of FPOs has formed a cooperative biomass plant that converts cotton stalks and sugarcane bagasse into pellets. This initiative provides additional income to farmers by buying their residues and processing them into high-demand fuel, creating jobs in the region and contributing to sustainable energy goals.
📌 Summary:
The biomass industry supports startups and FPOs by:
- Enabling biomass fuel production and waste-to-energy solutions
- Opening new revenue streams from waste residues
- Providing government support, investment opportunities, and job creation
This promotes sustainability, entrepreneurship, and economic empowerment for rural communities.

It’s remarkable in support of me to have a website, which is beneficial in favor of my knowledge.
thanks admin
Most Welcome