BIOMASS PELLETS VS FOSSIL FUELS: COST & ECO BENEFITS
Energy is the backbone of every industry—whether it’s manufacturing, food processing, pharmaceuticals, or power generation. Traditionally, industries in India and worldwide have relied heavily on fossil fuels like LPG (Liquefied Petroleum Gas), PNG (Piped Natural Gas), and Diesel. However, with rising fuel prices, supply fluctuations, and environmental concerns, biomass pellets have emerged as a sustainable, cost-effective, and eco-friendly alternative.
This blog explains the cost comparison, raw material availability, operational benefits, and environmental advantages of switching from fossil fuels to biomass pellets.
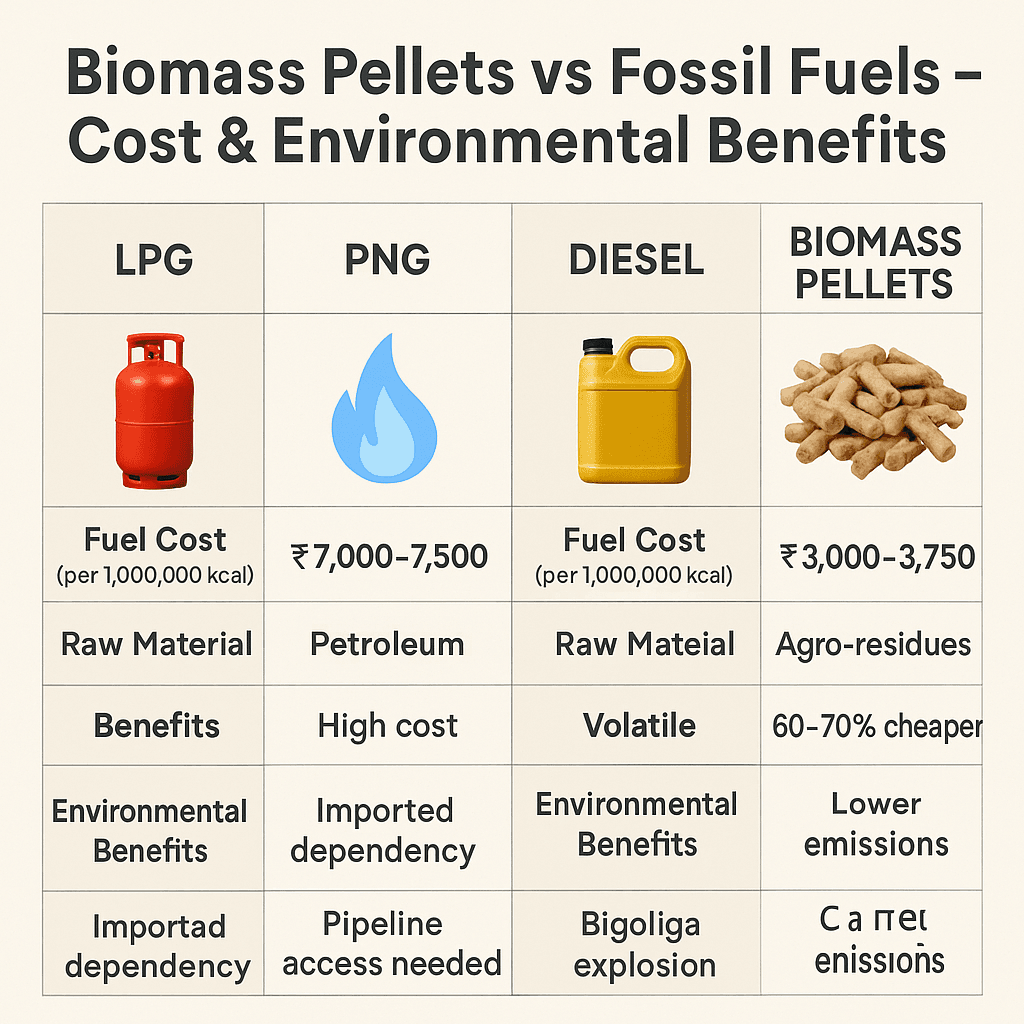
1. Fuel Cost Comparison – LPG, PNG, Diesel vs Biomass Pellets
| Fuel Type | Average Calorific Value (kcal/kg or kcal/ltr) | Current Market Price (India, 2025 est.) | Effective Cost per 1,000,000 kcal | Remarks |
| LPG | ~11,000 kcal/kg | ₹100–110/kg | ~₹9,000–10,000 | High cost, imported dependency |
| PNG | ~8,600 kcal/m³ | ₹60–65/m³ | ~₹7,000–7,500 | Price fluctuations, pipeline access needed |
| Diesel | ~10,000 kcal/ltr | ₹90–95/ltr | ~₹9,500–10,000 | Costly, volatile pricing, high emissions |
| Biomass Pellets | ~4,000 kcal/kg | ₹12–15/kg | ~₹3,000–3,750 | 60–70% cheaper than fossil fuels |
👉 Key Takeaway: Biomass pellets reduce fuel costs by up to 60% compared to LPG and Diesel, making them the most economical industrial heating option.
2. Raw Material Availability for Biomass Pellets
India is an agriculture-based economy, generating huge volumes of agro-residues every year. These residues form the base raw material for pellet manufacturing.
Common Raw Materials:
- Rice Husk & Paddy Straw – abundant in north & east India
- Groundnut Shells & Coconut Shells – available in coastal & southern states
- Sugarcane Bagasse – by-product of sugar mills in Maharashtra & Uttar Pradesh
- Sawdust & Wood Chips – from sawmills, furniture, and timber industries
- Corn Cobs & Stalks – widely available in central India
- Napier Grass & Energy Crops – cultivated as dedicated biomass crops
👉 With over 500 million tonnes of agricultural residue annually, India has an unlimited biomass supply to sustain pellet production.
3. Operational Benefits of Biomass Pellets
- Cost Savings – Lower fuel bills and faster return on investment (ROI).
- Stable Pricing – Unlike LPG and diesel, biomass pellet prices remain stable.
- Automation Ready – Modern biomass pellet burners and boilers come with automatic feeding systems, digital controls, and smoke collectors.
- High Efficiency – Up to 90% combustion efficiency with low maintenance.
- Versatility – Suitable for boilers, furnaces, dryers, ovens, and food processing.
4. Environmental Benefits of Biomass Pellets
- Carbon Neutral – CO₂ released during combustion equals the amount absorbed by plants during growth.
- Low Emissions – Minimal SOx, NOx, and particulate matter compared to diesel or coal.
- Compliance with Pollution Norms – Helps industries meet strict environmental regulations.
- Waste to Energy – Utilizes agricultural and industrial waste effectively.
- Reduced Carbon Footprint – Helps industries move towards net-zero targets.
5. Why Industries Should Switch to Biomass Pellets
- Cost Advantage – 50–70% fuel cost reduction.
- Availability – Abundant agro-residues ensure reliable supply.
- Government Support – Subsidies and policies promoting renewable energy.
- Sustainability Branding – Companies can market themselves as eco-friendly and green-certified.
- Energy Security – Reduces dependence on imported LPG, PNG, and Diesel.
6. Government Policies and Subsidies for Biomass Fuel
India is aggressively pushing bioenergy adoption under MNRE (Ministry of New and Renewable Energy) and state-level policies.
- Capital Subsidy Schemes – Available for biomass pellet plants and boilers.
- CPCB/State Pollution Control Norms – Encourage industries to switch from coal/diesel to clean fuels like biomass.
- Carbon Credits – Industries using biomass may qualify for carbon trading benefits.
- FAME & Net Zero Initiatives – Large industries aligning with “Net Zero 2070” goals are shifting to renewable fuels.
👉 This means companies adopting biomass today not only save money but also gain financial and regulatory advantages.
7. Technical Properties of Biomass Pellets
| Parameter | Biomass Pellets | LPG/PNG/Diesel |
| Moisture | < 10% | Not applicable |
| Density | 650–700 kg/m³ | Liquid/gaseous fuels |
| Ash Content | 1–5% (depending on raw material) | < 1% |
| Storage | Easy, requires dry area | Cylinders/tanks/pipelines |
| Safety | Non-explosive, safer to handle | Risk of explosion/fire |
👉 Pellets have stable combustion, safe storage, and easy handling, unlike volatile fossil fuels.
8. Industrial Applications of Biomass Pellets
- Food Industry – Bakery ovens, namkeen fryers, dairy processing.
- Pharmaceuticals & Chemicals – Steam boilers, dryers.
- Agro & Feed Industry – Grain dryers, cattle feed manufacturing.
- Metal Industry – Aluminium melting furnaces, heat treatment.
- Power Plants – Co-firing with coal for green electricity.
- Hotels & Institutions – Centralized hot water & cooking systems.
9. Biomass Supply Chain and Logistics
- Local Sourcing: Pellets are manufactured near agricultural clusters, reducing logistics costs.
- Storage Flexibility: Unlike PNG pipelines or diesel tanks, pellets can be stored in silos or bags.
- Transport Cost: Lower than LPG cylinders and diesel tankers.
- Decentralized Production: Pellet plants can be set up in villages, creating local employment.
10. Challenges & Solutions
- Ash Disposal – Solution: Ash can be used as fertilizer in agriculture.
- Moisture Control – Solution: Use modern dryers and proper storage.
- Awareness – Solution: Demonstrations and government-backed adoption programs.
- Initial Investment – Pellet burners/boilers may require capex, but ROI < 1 year due to fuel savings.
11. Future of Biomass Fuel in India
- India has set a target to replace 5–10% of fossil fuels in industries with biomass by 2030.
- IEA (International Energy Agency) projects biomass to be one of the fastest-growing renewable sources globally.
- Increasing demand for carbon-neutral fuels will make biomass pellets a mainstream industrial fuel.
- Rising corporate ESG commitments will further push industries towards biomass adoption.
Conclusion
- While LPG, PNG, and Diesel have been the traditional energy sources for industries, they are becoming unsustainable in terms of both cost and environmental impact. Biomass pellets offer a renewable, carbon-neutral, and cost-effective solution, helping industries achieve energy savings, regulatory compliance, and sustainability goals.
- Switch to Biomass Pellets – Save Costs, Save the Environment, and Secure the Future.